- Software
- Zencrack
- What’s New in Zencrack?
Zencrack 9.1-1
What's New in Zencrack?
Zencrack 9.1-1
Zencrack version 9.1-1 was finalised on 17 November 2022
The highlights for this release are:
- full support for the Zencrack remeshing capability in the interface to Ansys
- first availability of Zencrack version 9 for Linux including, for the first time, a Linux version of the Zencrack GUI.
Remeshing in the Ansys interface
The new remeshing capability provided for the Abaqus interface in Zencrack 9.0-1 is now fully supported for the Ansys interface. The remeshing capability provides mesh independent crack insertion into an uncracked mesh. This approach simplifies the creation of 3D models containing cracks by using a purely geometric definition of an initial crack.
An existing uncracked mesh can be used "as-is" with, in most cases, no need to perform special partitioning or meshing of the uncracked geometry. This means that, for example, a single uncracked mesh can be used to develop models of significantly different cracks by simply changing the geometric crack definition.
- initial crack and crack growth
- remeshing for analysis of initial crack only
- remeshing for general non-planar 3D crack growth using the existing load system methodologies in Zencrack for fatigue, time dependent and combined fatigue/time crack growth prediction
- geometric definition of an initial crack
- initial crack location is fully independent of the underlying mesh
- the underlying mesh may contain hex or tet elements
- crack at a symmetry plane, surface breaking or fully embedded
- initial crack shape may be straight or elliptic (either full ellipse or elliptic arc)
- remeshed region split into hex rings and surrounding tets
- rings of hex elements at the crack front with ring mesh density controlled by the user
- tet mesh surrounding the rings
- fully automatic calculation of the extent of the remeshed tet region and mesh density within that region (with manual control if desired)
- support for static, thermal and coupled analyses
- update of displacement boundary conditions, pressure loads, surface definitions, film coefficients and temperatures in the remesh region
- optional application of pressure and/or film coefficients to the crack face
The remeshing capability is fully supported in the Zencrack GUI with options to preview various aspects of the initial crack definition, including:
- option to define geometric positional data by picking nodes in the uncracked mesh
- preview of the geometric crack definition
- preview of the hex rings at the crack front
- preview of the remesh region
- preview of the remesh region with the crack inserted
Linux Version of Zencrack
Zencrack version 8.3-1 (and earlier releases) included availability of the Zencrack analysis code for 64-bit Linux platforms. When version 9.0-1 was released no Linux version was provided as development effort was placed on the remeshing methodology.
With the version 9.1-1 release comes support on Linux platforms for the Zencrack analysis code and the Zencrack GUI.
The Linux version has been tested with Abaqus and Ansys on three Linux variants:
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 7.9
- with Abaqus 2022, Ansys 2022 R2
- CentOS Linux release 8.5.2111
- with Abaqus 2022, Ansys 2022 R2
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Desktop 12 SP3
- with Abaqus 2020, Ansys 2021 R2
Linux Version of the Zencrack GUI
For the first time the Zencrack GUI is available on Linux platforms. This provides the same capabilities as the Windows version including full support for interactive remeshing previews.
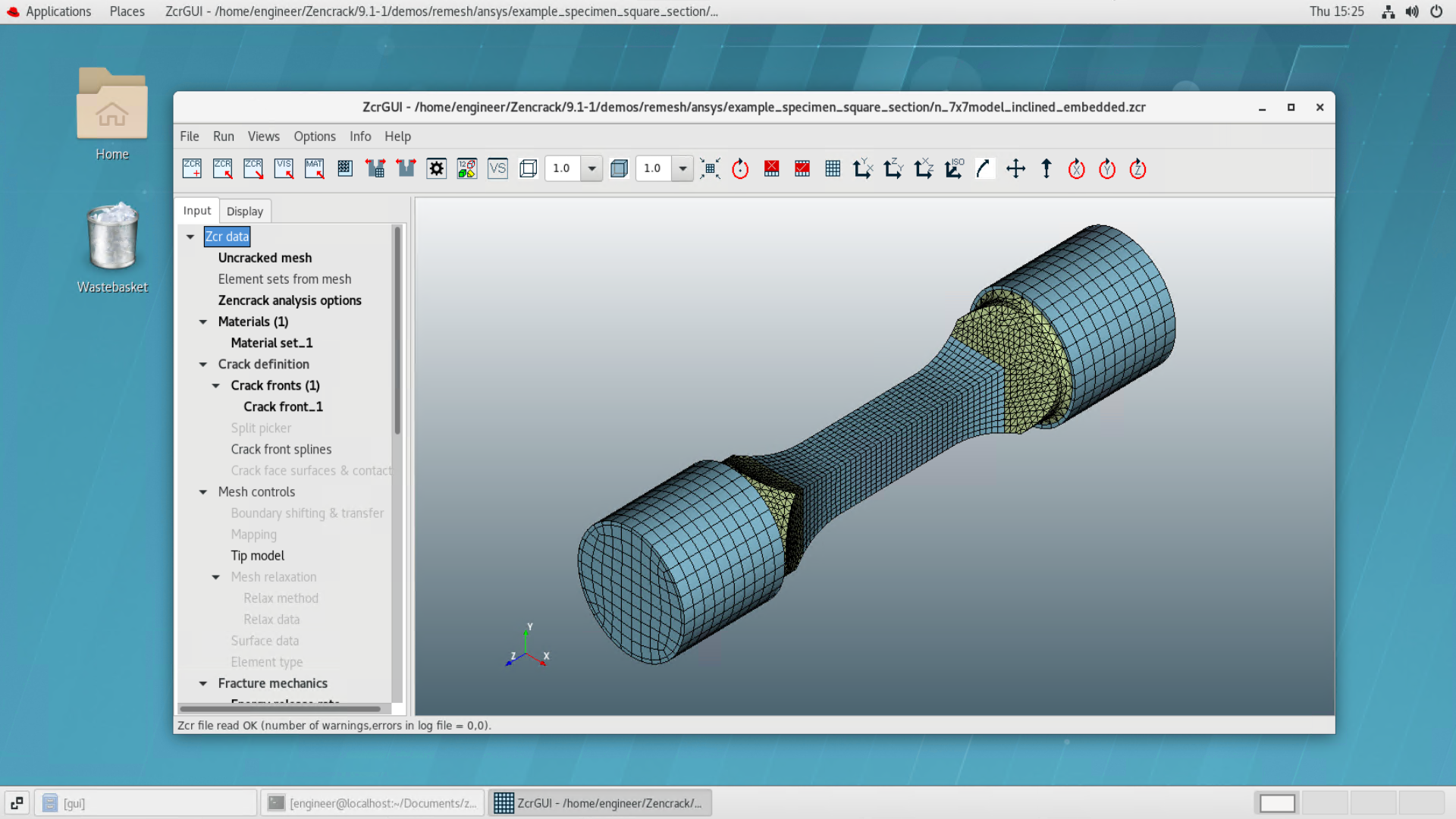
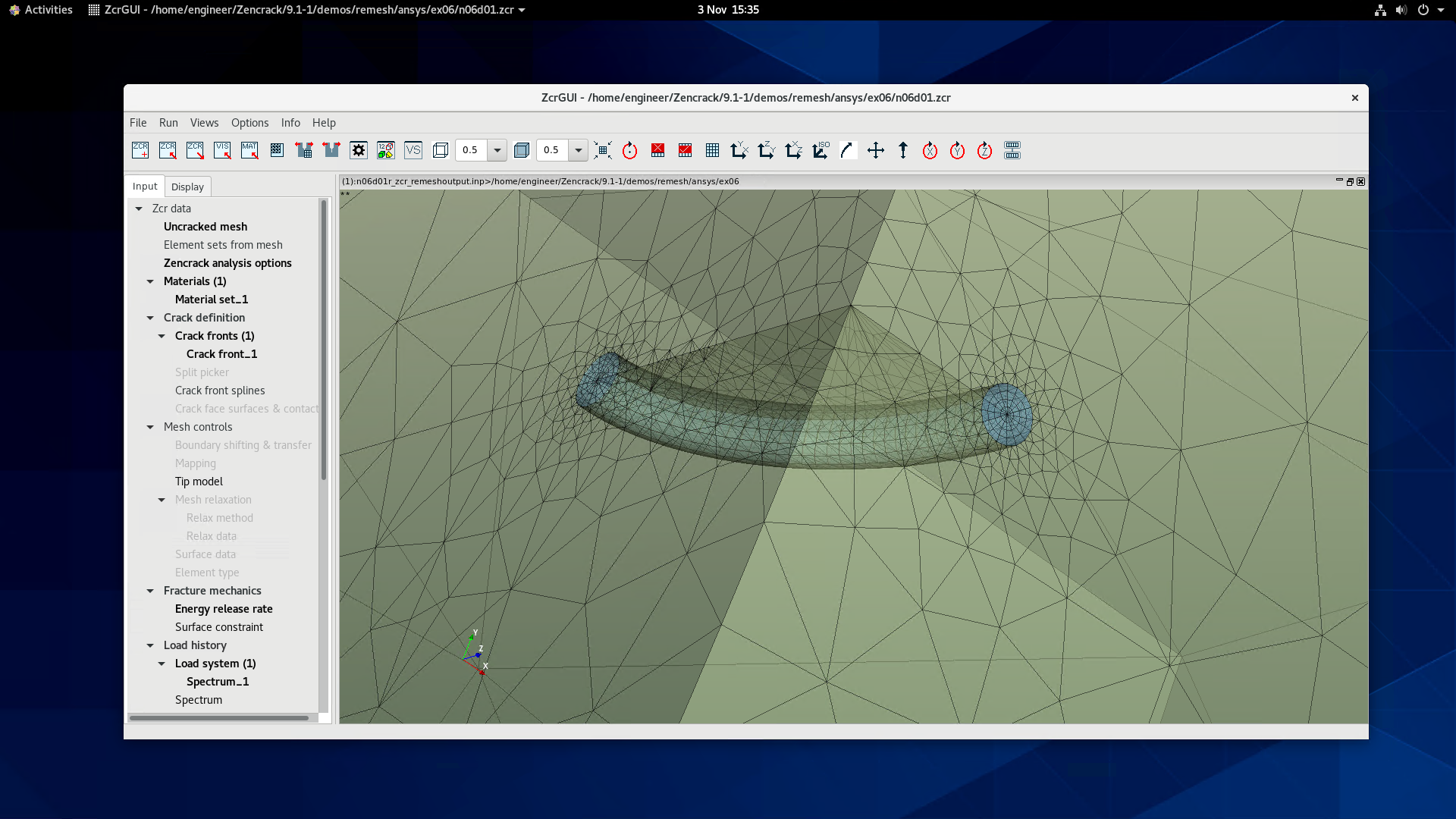
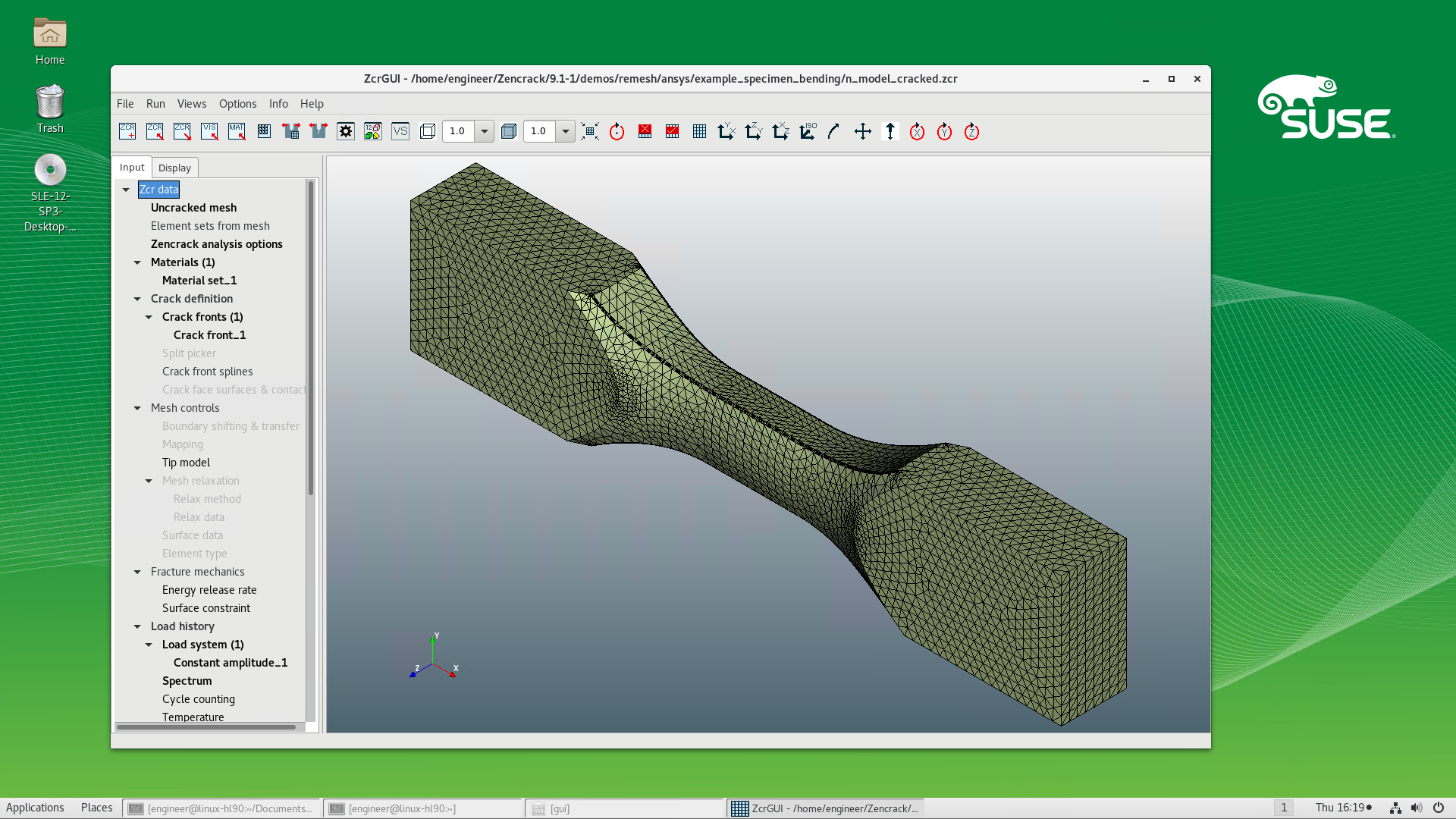
Zencrack GUI Enhancements
When an Ansys model is imported to the GUI it may be necessary to run Ansys:
- to enable import of node and element components,
- to generate mesh data if the model contains only solid model commands.
In version 9.1-1 the RUNANSYS parameter which controls import of Ansys models to the GUI is modified to have three values: Yes, No and Automatic. The Yes and No options now force that Ansys is always or never executed during import, regardless of the model definition. So for example, if the option is set to No and the model contains only solid model commands and no explicit mesh, the import will fail because Ansys is not executed. A setting of Yes or Automatic for the same model would run Ansys and result in a successful import. The Automatic option has some changes to reduce the number of reasons that would trigger the need for running Ansys. In most cases the default setting of RUNANSYS=No is recommended as it produces the fastest model import to the GUI.
In version 9.0-1 an option to render meshes with "colour by material id" was added to identify regions by material id. This was supported for Abaqus models in which the NAME parameter from *MATERIAL keywords is displayed.
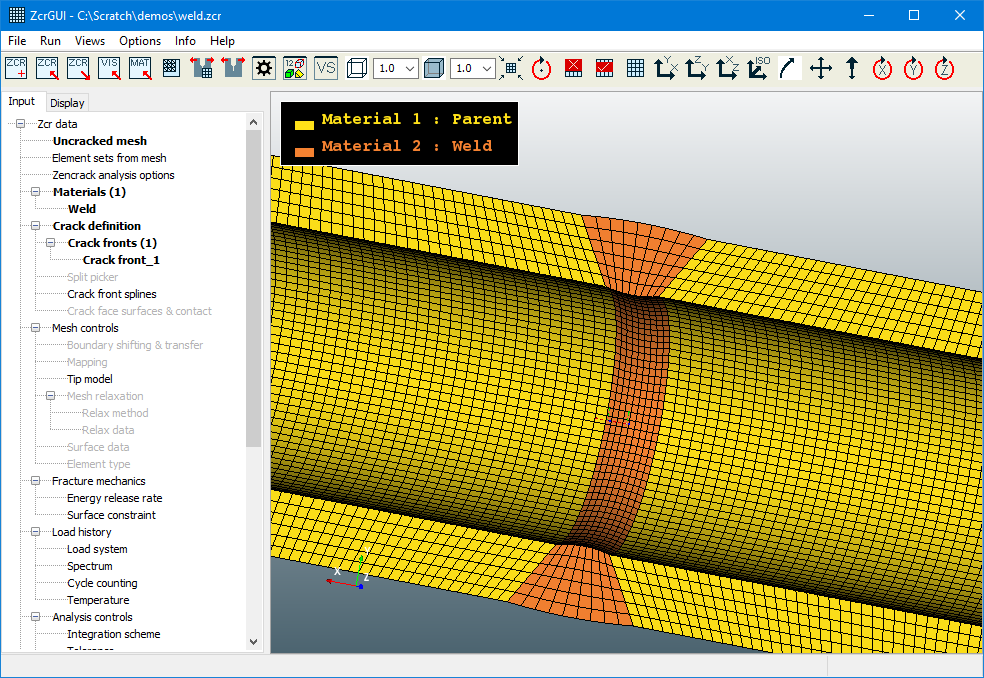
In version 9.1-1 material ids are also available when an Ansys mesh is imported to the GUI. The integer values from the MAT keywords are displayed. If no material is defined when an element is processed during import the id for that element is set to 1 (which is the behaviour applied by Ansys).
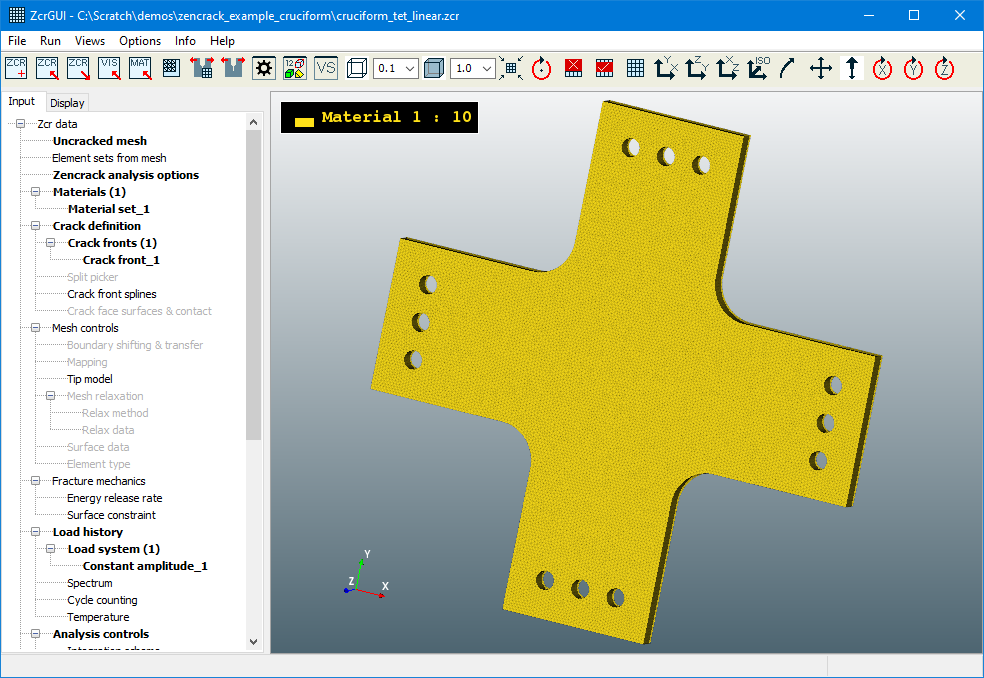
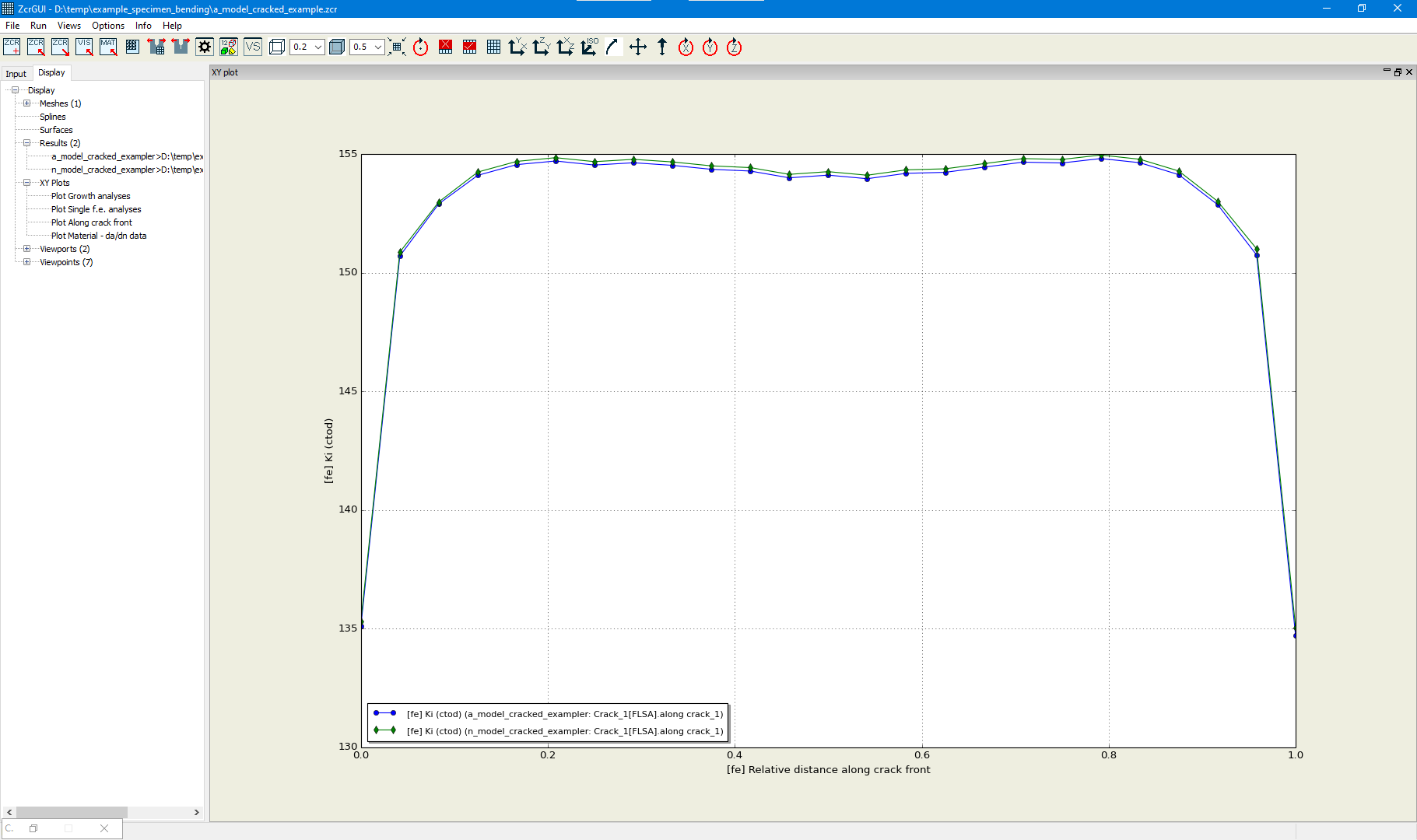
Remeshing Example - Abaqus vs Ansys
An example is shown of the same crack introduced in Abaqus and Ansys models of a test specimen using the remeshing method. The only change in the Zencrack input file for the two analyses is the reference to the uncracked mesh filename.
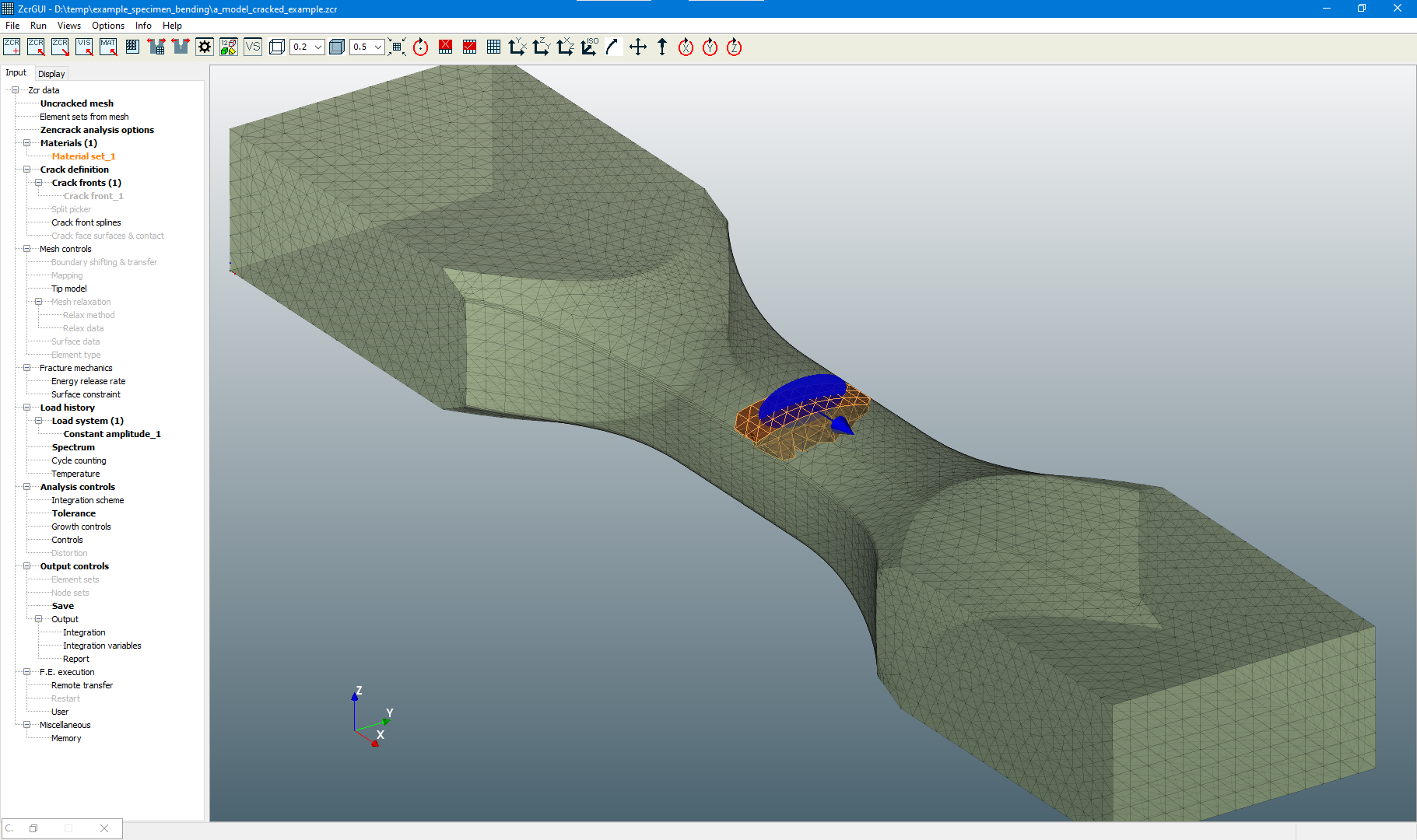
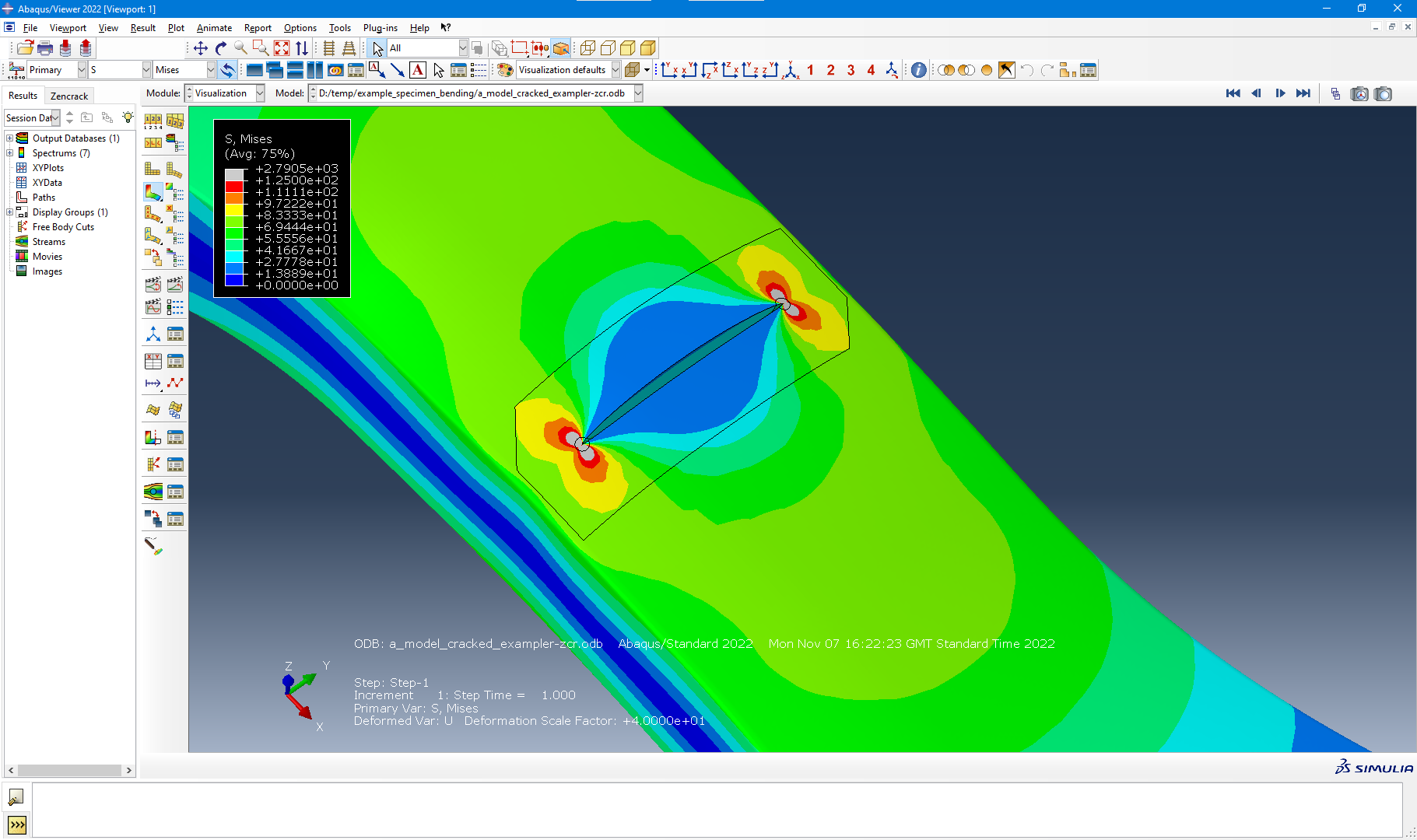
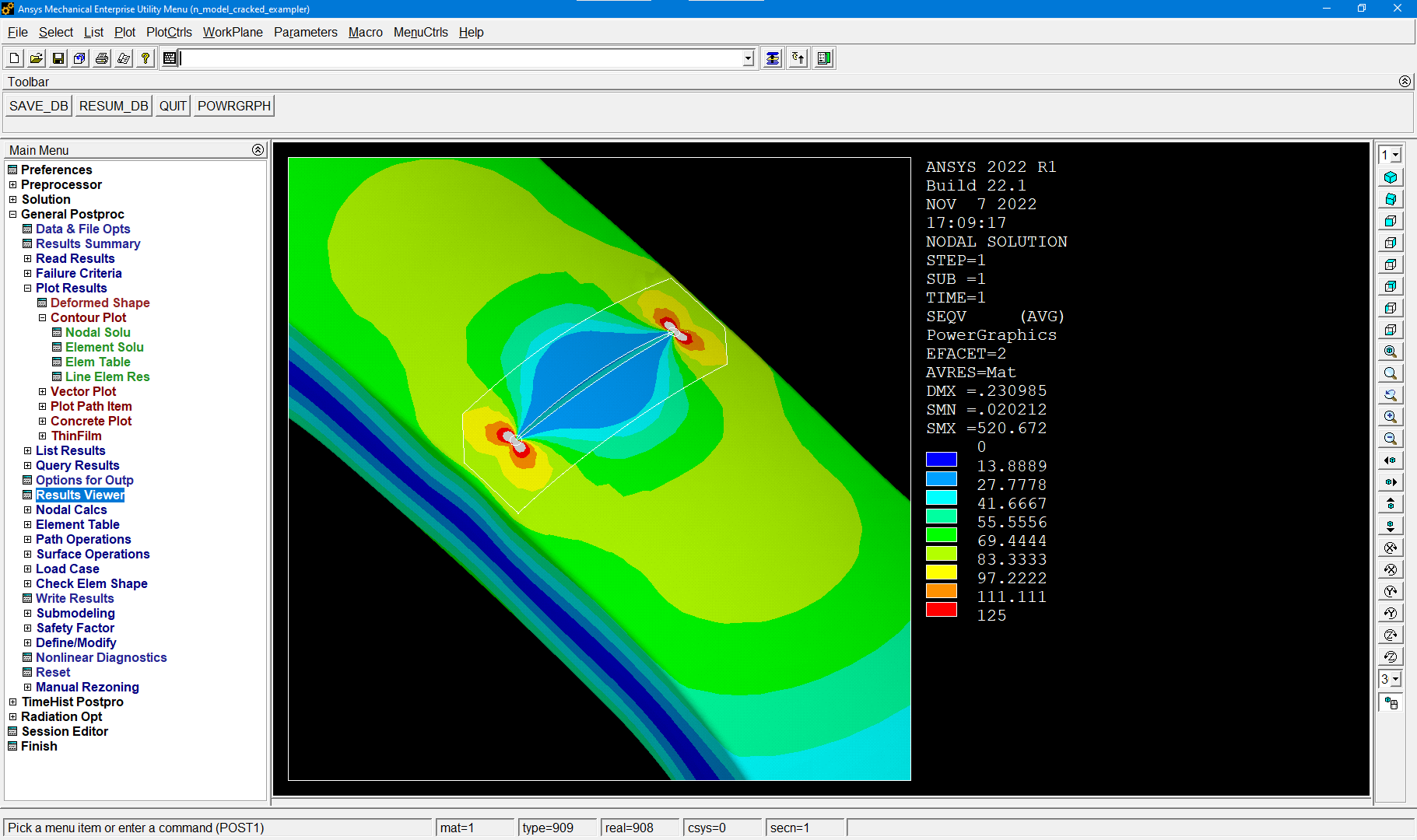
Miscellaneous Enhancements
Remeshing
- Improved ring radius controls - allows automatic reduction of ring radius when meshing produces invalid ring
- Prevention of embedded cracks protruding from a model - new ring-to-surface intersection checks to prevent rings falling outside the mesh bound
- Prevention of entity numbering clashes - better processing of node and element numbers in the remesh region to avoid clashing with the uncracked mesh
- Additional checks for gaps in the crack plane - detect and resolve cases where the processing of the crack plane may result in small gaps
Others
- The *SPECTRUM keyword previously allowed up to 80 load systems to be defined on a single dataline. It is modified to allow any number of load systems in the spectrum sequence with input of up to 80 items per dataline across multiple datalines.
- The crack-block method adds support for Ansys element SOLID225.
- The coordinate precision is increased when creating the .xyz file from a pre-pass Ansys run. The old format, 16.8, is changed to use 21.13 format which is documented in Ansys 2022 R1 as the format used when the NWRITE command is used: (I9, 6G21.13E3).
- A blank entry for the LKEY on Ansys SFE options previously meant the data was passed unchanged into the cracked mesh. Now a blank entry is converted to the Ansys default of 1 to allow the option to be processed for updates.
- The uncracked mesh name can be extracted from a new common block, JOBuc, in user subroutines. The existing common block JOBin has one variable added defining the job folder (i.e. path only).